1. 참고자료
1.1 링크
1.1.1 논문
더보기
1.1.2 홈페이지
더보기
https://robin-lab.cs.utexas.edu/BUMBLE
BUMBLE: Unifying Reasoning and Acting with VLMs for Building-Wide Mobile Manipulation
To operate at a building scale, service robots must perform very long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks by navigating to different rooms, accessing different floors, and interacting with a wide and unseen range of everyday objects. We refer to these tasks
robin-lab.cs.utexas.edu
2. 논문 내용 정리
2.1 Figure1

2.1.1 Building-wide mobile manipulation
더보기
- building scale에서 작동하기 위해, service robots은 다음을 수행함
- long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks
- navigating to different rooms
- accessing multiple floors
- interacting with a wide and unseen range of everyday objects
- long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks
- Example
- user instruction: "I am on a diet, but I want soda"
- robot:
- interpret the free-form instruction
- create high-level task plan to accomplish the task
- instantiate low-level robot commands to achieve it
- 로봇은 kitchen으로 이동해야 할 수도 있고, 다른 층에 있다면 엘리베이터를 이용해야 할 수도 있다.
- 엘리베이터를 사용하려면 무조건 사전의 엘리베이터 사용 experiences을 활용해야 함
- 로봇은 좁은 복도를 막고 있는 물건을 밀거나 방 안팎으로 이동하기 위해 문을 여는 것과 같이 예상치 못한 장애물을 처리해야 할 수도 있다.
- 로봇이 주방에 도착한 후에, 적절한 다이어트 소다 캔을 식별해야 함
- 이전에 본 적 없더라도, "diet" option을 인식해야 함..
- building scale mobile manipulation의 requirements
- an open-world perception system: reasoning about diverse objects
- complex motor skills: to act effectively in buildings
- memory: for temporally extended reasoning in long-horizon task execution
2.1.2 BUMBLE
더보기
- BUilding-wide MoBiLE Manipulation
- unified Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based framework
- open-world RGB-D perception
- a wide spectrum of gross-to-fine motor skills
- dual-layered memory
- four key infredients
- VLM: serving as the central reasoning module
- connecting perception, memory, and, skills
- dual-layered memory
- short-term memory: to maintain robot execution history
- long-term memory: to store valuable experience and concepts from past trials
- a diverse skill library of parameterized skills
- 로봇이 다른 층 및 방으로 navigate 하도록 함
- ex) GoToLandmark[GoalImage], UseElevator[Button]
- manipulation을 위한 robot base adjust
- ex) MoveBase[Dir.]
- diverse contact-rich behaviours를 통한 objects와 상호작용
- ex) PushObjOnGround[ObjSeg., Dir.]
- 로봇이 다른 층 및 방으로 navigate 하도록 함
- perception system
- open-world, cluttered scenes을 시각적으로 reason
- embodied decisions을 위해 필요한 depth information을 process
- VLM: serving as the central reasoning module
2.2 Figure2

2.3 Figure3

2.3.1 key technical blocks of BUMBLE
더보기
총 2개의 key technical blocks으로 구성된 상태
- (a): Perception System, Skill Library, and Memory
- open-world perception
- a library of diverse skills: physical world에서 act 하기 위함
- short and long-term memory: 실시간 적응(adaptation) 및 past mistakes로부터 learning
- (b): VLM-based Decision making module
- current scene에 text instruction을 ground하고 reason
- 실행할 next parameterized skill을 predict
2.3.2 Perception System, Skill Library, and Memory
더보기





- Open-World Perception System
- robots은 open-world objects를 percieve 및 localize 해야함
- robust segmentation model을 갖춘 perception system을 사용
- Grounded-SAM (GSAM): segmenting foreground interactable objects
- VLM에 querying 하는 것 대신 사용
- more precise localization 및 manipulation을 가능하게 함
- segmentation models은 pixel-level accuracy 제공하기 때문
- scene에 대한 object masks를 얻은 후, depth images를 back-projecting 해서 object point cloud 계산
- robot 및 detected objects 사이의 precise disdtance 계산
- Grounded-SAM (GSAM): segmenting foreground interactable objects
- robust segmentation model을 갖춘 perception system을 사용
- robots은 open-world objects를 percieve 및 localize 해야함

- Skill Library
- diverse skill library
- high-level abstract behaviours: ex) navigating to a room
- more fine-grained behaviours: ex) adjusting the base for manipulation
- ex) GoToLandmark, NavigateNearObj, MoveBase, Pickup, PushObjOnGround, OpenDoor, CallElevator, and UseElevator.
- GoToLandmark를 제외하고는, each skill의 parameters는 object 또는 robot configurations에 따라 결정됨
- building의 topological visual map 사용
- landmark images를 nodes로, 2D occupancy maps을 nodes 사이의 trajectories를 생성하는 데 사용
- library of parameterized skills 및 VLM의 reasoning capabilites를 활용하여, subtask 및 skill을 예측하고 skill parameters를 추정하여 로봇의 motion을 결정
- building-wide tasks를 수행하기 위한 semantic 및 geometric reasoning을 task level에서 통합
- diverse skill library


- Memory
- 로봇이 state-action history를 추적할 수 있게 하고, failed skill executions으로부터 recover할 수 있도록 함
- ex) failed grasping attempt 후에 moving obstacles 또는 adjusting the base
- 종류
- short-term memory
- current execution trial의 each prediction step에서 다음을 저장
- scene image
- subtask
- skill name
- parameter
- system detected execution result (success/failure)
- VLM이 next skill을 예측할 때 entire execution history를 기반으로 추론할 수 있게 함
- long-horizon building-wide tasks에 중요
- current execution trial의 each prediction step에서 다음을 저장
- long-term memory: BUMBLE이 추론 과정에서의 실수로부터 학습하도록 함 -> 실수 감소
- 이전에 수집된 prediction failures (fail 여부는 사람이 판단)
- description context
- user instruction, scene image, predicted subtask, skill name, predicted parameters
- failure reason에 대한 VLM text analysis
- serving as lessons for improving future predictions 및 reducing the dependency on humman annotations
- description context
- 이전에 수집된 prediction failures (fail 여부는 사람이 판단)
- short-term memory
- 로봇이 state-action history를 추적할 수 있게 하고, failed skill executions으로부터 recover할 수 있도록 함
2.3.3 VLM-based Decision Making
더보기
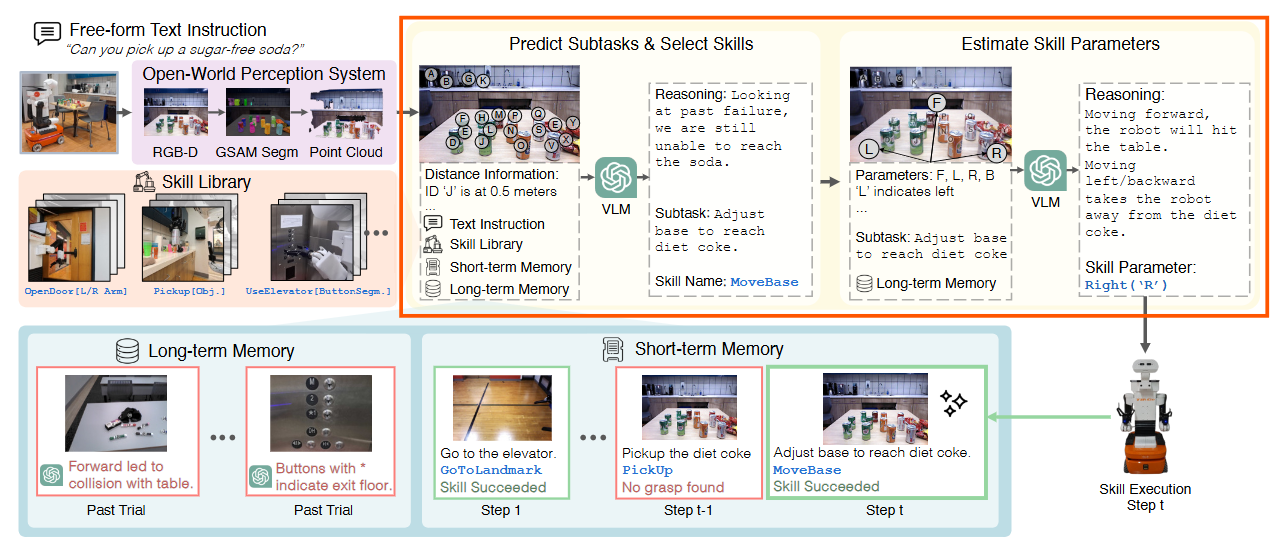

- 이 파트는 다음에 정리해도 될 듯